二叉堆数据结构
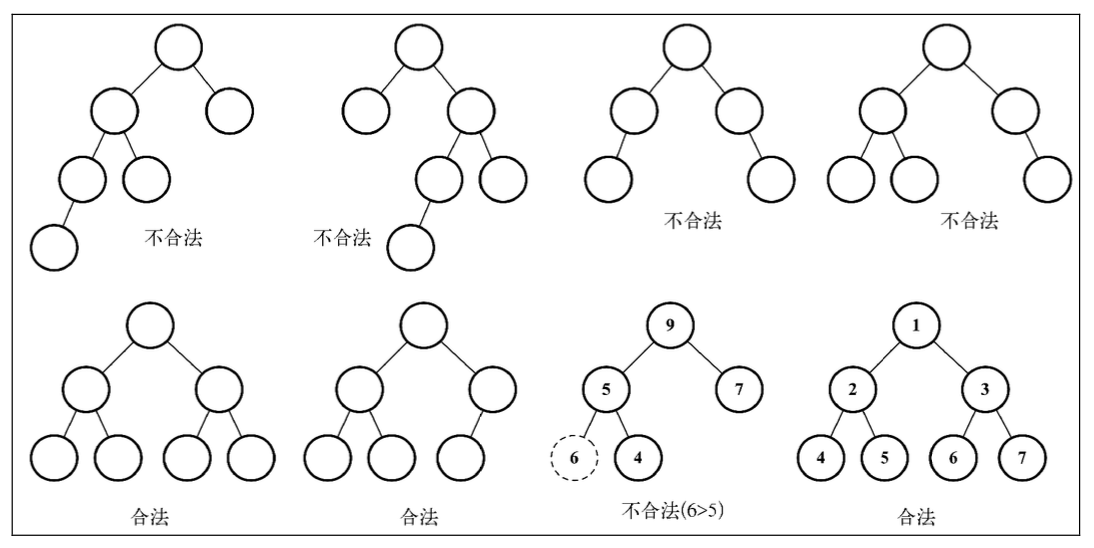
二叉堆是一种特殊的二叉树,有以下两个特性:
- 它是一棵完全二叉树,表示树的每一层都有左侧和右侧子节点(除了最后一层的叶节点), 并且最后一层的叶节点尽可能都是左侧子节点,这叫作结构特性
- 二叉堆不是最小堆就是最大堆。最小堆允许你快速导出树的最小值,最大堆允许你快速 导出树的最大值。所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或小于等于(最小堆)每个它的子节点。这叫作堆特性。
创建最小堆类
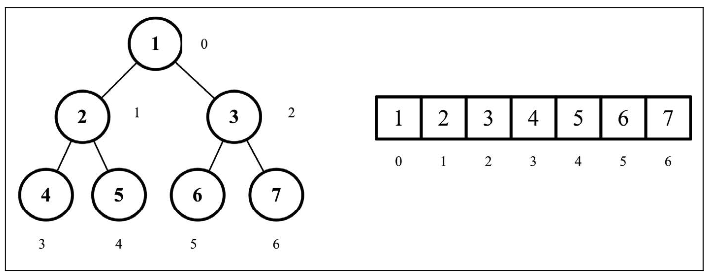
二叉树的数组表示
二叉树有两种表示方式。第一种是使用一个动态的表示方式,也就是指针(用节点表示), 在上一章使用过。第二种是使用一个数组,通过索引值检索父节点、左侧和右侧子节点的值。下图展示了两种不同的表示方式。
我们将会使用数组来存储数据
1 | class MinHeap { |
向堆中插入值
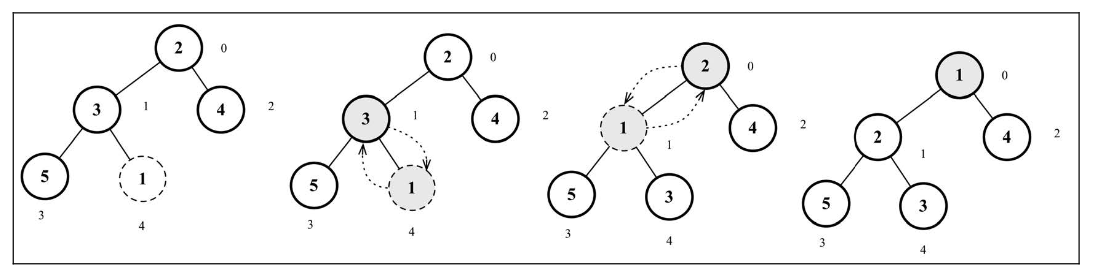
向堆中插入值是指将值插入堆的底部叶节点再执行 siftUp 方法,表示我们将要将这个值和它的父节点进行交换,直到父节点小于这个插入的值。这个上移操作也被称为 up head、percolate up、bubble up、heapify up 或 cascade up。
1 | insert(value) { |
导出堆中的最小值或最大值
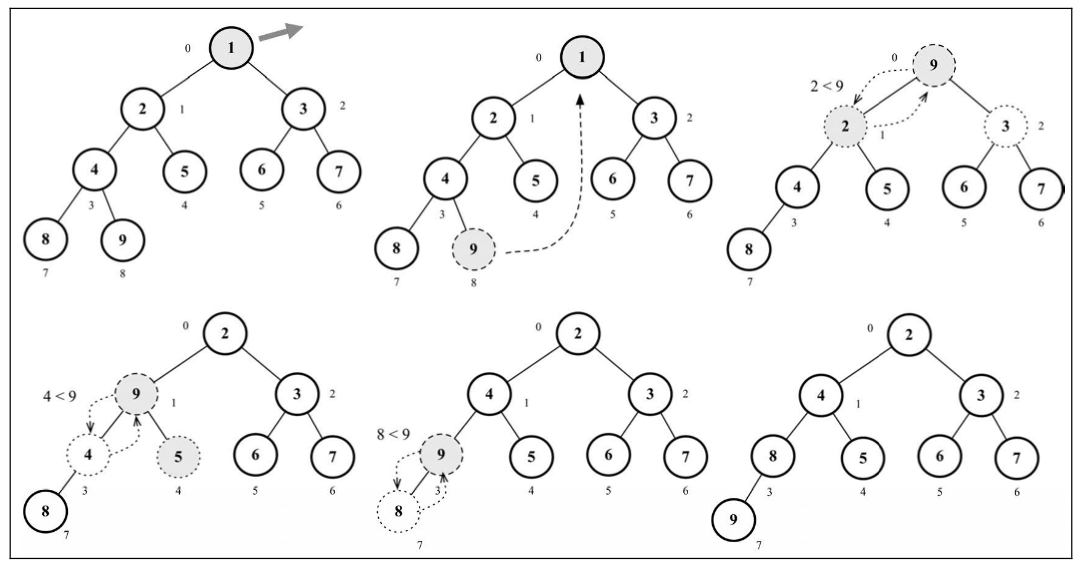
移除最小值(最小堆)或最大值(最大堆)表示移除数组中的第一个元素(堆的根节点)。 在移除后,我们将堆的最后一个元素移动至根部并执行 siftDown 函数,表示我们将交换元素直到堆的结构正常。这个下移操作也被称为 sink down、percolate down、bubble down、heapify down 或 cascade down。
1 | extract() { |
创建最大堆类
可以扩展 MinHeap 类来继承我们在本章创建的所有代码,并在需要时进行反向的比较
1 | function reverseCompare(compareFn) { |
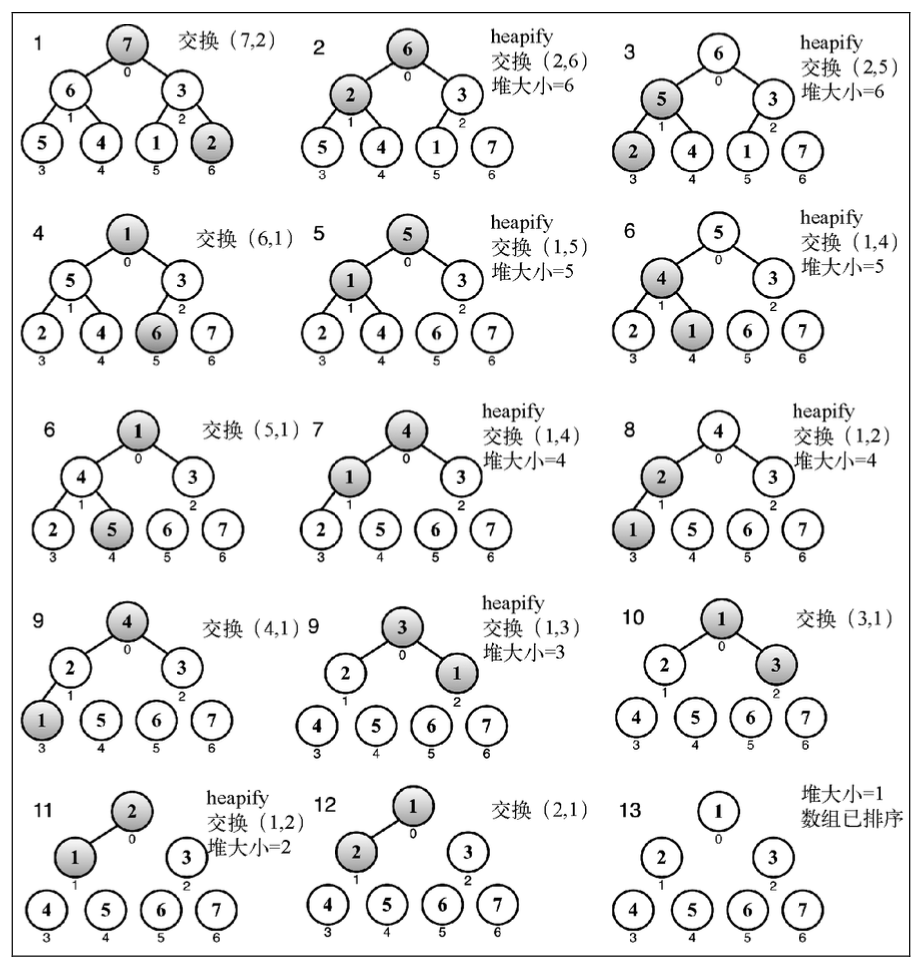
堆排序算法
我们可以使用二叉堆数据结构来帮助我们创建一个非常著名的排序算法:堆排序算法。它包含下面三个步骤。
- 用数组创建一个最大堆用作源数据。
- 在创建最大堆后,最大的值会被存储在堆的第一个位置。我们要将它替换为堆的最后一个值,将堆的大小减 1。
- 最后,我们将堆的根节点下移并重复步骤 2 直到堆的大小为 1。
我们用最大堆得到一个升序排列的数组(从最小到最大)。如果我们想要这个数组按降序排列,可以用最小堆代替。
1 | function heapSort(array, compareFn = defaultCompare) { |
最大堆函数会重新组织数组的顺序。归功于要进行的所有比较,我们只需要对后半部分数组 执行 heapify(下移)函数(前半部分会被自动排好序,所以不需要对已经知道排好序的部分 执行函数)。
heapify 函数和我们创建的 siftDown 方法有相同的代码。不同之处是我们会将堆本身、 堆的大小和要使用的比较函数传入作为参数。这是因为我们不会直接使用堆数据结构,而是使用 它的逻辑来开发 heapSort 算法。
堆排序算法不是一个稳定的排序算法,也就是说如果数组没有排好序,可能会得 到不一样的结果。