- 继承分为:接口继承、实现继承
- 接口继承:只继承方法签名
- 实现继承:继承实际方法
- ECMAScript只支持实现继承,依靠原型链实现。
1.原型链
- 基本思想:利用原型让一个引用类型继承另一个引用类型的属性和方法。
- 基本方法:让原型对象等于另一个类型的实例。
- 基本模式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21function SuperType(){
this.property=true;
}
SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue=function(){
return this.property;
}
function SubType(){
this.subproperty=false;
}
//继承SuperType
SubType.prototype=new SuperType();
SubType.prototype.getSubValue=function(){
return this.subproperty;
}
var instance=new SubType();
alert(instance.getSuperValue()); //true
关系如图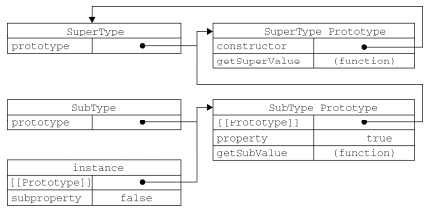
- 通过实现原型链,本质上扩展了本章前面介绍的原型搜索机制。沿着原型链逐渐向上搜索。
1.1 别忘记默认的原型
- 所有引用类型都默认继承了Object。
- 所有函数的默认原型都是Object的实例。
完整原型链如下: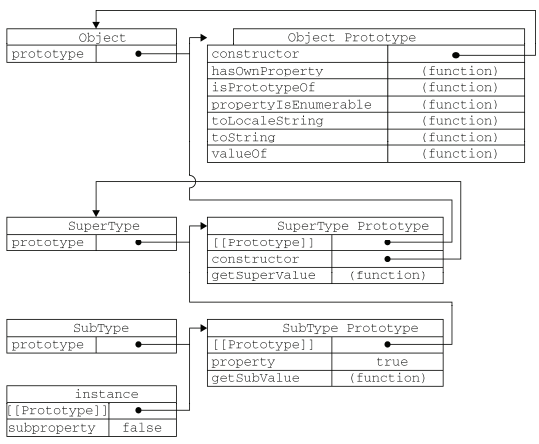
1.2 确定原型和实例的关系
instanceof操作符:测试实例与原型链中出现过的构造函数,结果就会返回true.1
2
3alert(instance instanceof Object); //true
alert(instance instanceof SuperType); //true
alert(instance instanceof SubType); //trueisPrototypeOf()操作符:只要是原型链中出现过的原型,都可以说是该原型链派生的实例的原型。1
2
3alert(Object.prototype.isPrototypeOf(instance)); //true
alert(SubType.prototype.isPrototypeOf(instance)); //true
alert(SuperType.prototype.isPrototypeOf(instance)); //true
1.3 谨慎的定义方法
给原型添加方法的代码一定要在替换原型的语句之后。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28function SuperType(){
this.property=true;
}
SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue=function(){
return this.property;
}
function SubType(){
this.subproperty=false;
}
//继承SuperType
SubType.prototype=new SuperType();
//添加新方法
SubType.prototype.getSubValue=function(){
return this.subproperty;
}
//屏蔽超类型中的同名属性,相当于在SubType.prototype中创建一个同名属性,通过超类型调用此属性还是原来的属性。
SubType.prototype.getSuperValue=function(){
return false;
}
var instance=new SubType();
alert(instance.getSuperType()); //false通过原型链实现继承时,不能使用对象字面量创建原型方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28function SuperType(){
this.property=true;
}
SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue=function(){
return this.property;
}
function SubType(){
this.subproperty=false;
}
//继承SuperType
SubType.prototype=new SuperType();
//使用字面量添加新方法,会导致上一行代码无效,因为重写了原型对象
SubType.prototype={
getSubValue:function(){
return this.subproperty;
},
someOtherMethod:function(){
return false;
}
};
var instance=new SubType();
alert(instance.getSuperValue()); //error
1.4 原型链的问题
包含引用类型值的原型。在对包含引用类型值的属性做修改后,会间接通过继承被所有实例共享并反映出来。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16function SuperType(){
this.colors=["red","blue","green"];
}
function SubType(){
}
SubType.prototype=new SuperType();
var instance1=new SubType();
instance1.colors.push("black");
alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black"
var instance2=new SubType();
alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green,black"在创建子类型实例时,不能向超类型的构造函数传递参数。
实践中很少单独使用原型链
2.借用构造函数
- 基本思想:在子类型构造函数的内部调用超类型构造函数
如下所示1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15function SuperType(){
this.colors=["red","blue","green"];
}
function SubType(){
//继承了SuperType
SuperType.call(this);
}
var instance1=new SubType();
instance1.colors.push("black");
alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black"
var instance2=new SubType();
alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green"
2.1传递参数
- 相比原型链,借用构造函数可以在子类型中向超类型构造函数传递参数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15function SuperType(){
this.colors=["red","blue","green"];
}
function SubType(){
//继承了SuperType,同时还传递来参数
SuperType.call(this,"Nicholas");
//实例属性
this.age=29;
}
var instance=new SubType();
alerrt(instance.name); //"Nicholas"
alert(instance.age); //29
2.2借用构造函数的问题
- 和构造函数模式存在问题一样——方法都在构造函数中定义,无法复用函数
- 在超类型的原型中定义的方法,对子类型而言也是不可见的。因为此时构造函数被当作普通函数来用。
3.组合继承
最常用的继承模式。
思路:使用原型链实现对原型属性和方法的继承,而通过借用构造函数来实现对实例属性的继承。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32function SuperType(name){
this.name=name;
this.colors=["red","blue","green"];
}
SuperType.prototype.sayName=function(){
alert(this.name);
};
function SubType(name,age){
//继承属性
SuperType.call(this,name);
this.age=age;
}
//继承方法
SubType.prototype=new SuperType();
SubType.ptototype.constructor=SubType;
SubType.ptototype.sayAge=function(){
alert(this.age);
}
var instance1=new SubType("Nicholas",29);
instance1.colors.push("black");
aler(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black"
instance.sayName(); //"Nicholas"
instance1.sayAge(); //29
var instance2=new SubType("Greg",27);
alert(instance.colors); //"red,blue,green"
instance2.sayName(); //"Greg"
instance2.sayAge(); //27instanceof、isPrototypeOf()都能够适用
4.原型式继承(后面2种继承的基础)
什么场景用?没有必要创建构造函数,而只想让一个对象与另一个对象保持类似情况下。
思路:借助原型可以基于已有对象创建新对象,同时不必因此创建自定义类型。
object()对传入其中的对象执行一次浅复制(浅复制指只是复制给原型对象?)
函数如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22//基本模式
function object(o){
function F(){}; //创建临时性构造函数
F.prototype=o;
return new F(); //返回这个临时类型的一个实例
}
//例子
var person={ //作为另一个对象的基础
name:"Nicholas",
friends:["Shely","Court","Van"]
};
var anotherPerson=object(person);
anotherPerson.name="Greg";
anotherPerson.friends.push("Rob");
var yetAnotherPerson=object(person);
yetAnotherPerson.name="Linda";
yetAnotherPerson.friends.push("Barbie");
alert(person.friends); //"Shely,Court,Van,Rob,Barbie"这种原型式继承,必须有一个对象作为另一个对象的基础。
ECMAScript5新增
Object.create()。
5.寄生式继承
- 什么场景用?主要考虑对象而不是自定义类型和构造函数的情况下
- 思路:创建一个仅用于封装继承过程的函数,该函数在内部以某种方式来增强对象,最后再返回对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7function createAnother(original){
var clone=object(original); //调用原型式继承的函数创建一个新对象
clone.sayHi=function(){ //以某种方式加强
alert('hi');
};
return clone; //返回这个对象
}
6.寄生组合式继承
- 组合继承的问题:无论什么情况下,都会调用两次超类型构造函数:第一次是在创建子类型原型的时候,第二次是在子类型构造函数内部,
所以在调用子类型构造函数时会重写超类型对象的全部实例属性。两次调用,第一次调用会将超类型的实例属性传递给子类型的原型,第二次调用则将超类型的实例属性传递给子类型实例。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22function SuperType(name){
this.name=name;
this.colors=["red","blue","green"];
}
SuperType.prototype.sayName=function(){
alert(this.name);
};
function SubType(name,age){
SuperType.call(this,name); //第二次调用SuperType()
this.age=age;
}
SubType.prototype=new SuperType(); //第一次调用SuperType()
SubType.ptototype.constructor=SubType;
SubType.ptototype.sayAge=function(){
alert(this.age);
}
var instance1=new SubType("Nicholas",29);
如图所示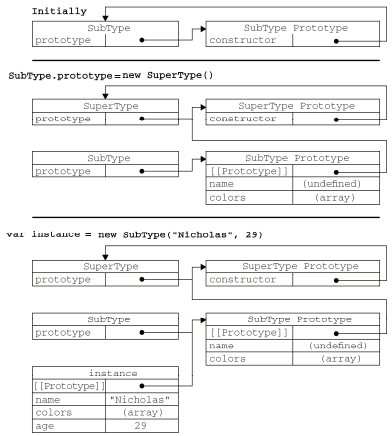
- 什么是寄生组合式继承:通过借用构造函数来继承(实例)属性,通过原型链的混成形式来继承方法。
- 思路:不必为了指定子类型的原型而调用超类型的构造函数,我们所需要的无非就是超类型原型的一个副本而已。
- 本质:使用寄生式继承来继承超类型的原型,然后再将结果指定给子类型的原型。
- 引用类型最理想的继承范式,能使用
instanceof和isPrototypeOf()方法
1 | 基本模式如下 |
